Java List 介紹
List
架構圖
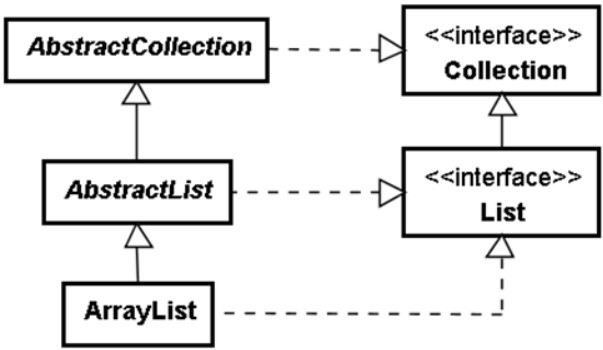
在JAVA SE 中,除了提供實作也也提供了abstract class 來作為擴充需求
具具有索引的 List
有兩種類別
- ArrayList
- LinkedList
List 介面定義了 add、remove、set 等許多依索引操作的方法。java.util.LinkedList 也實作了 List 介面,什麼時候該用 ArrayList?何時該用 LinkedList 呢?
ArrayList
特點:
- 隨機訪問:由於基於數組,所以可以快速訪問任何位置的元素(即隨機訪問)。
- 性能:添加(尾部)、刪除(尾部)和獲取元素的操作非常快,但在列表中間或開頭添加或刪除元素可能較慢,因可能導致數據移動。
- 內存使用:會在內部數組大小達到其容量上限時自動增長,但可能會有一些內存浪費,尤其是數組大小遠大於實際需要時。
範例:
1 | |
LinkedList
在 LinkedList 內部使用 Node 封裝新增的物件,每次 add 新增物件之後,將會形成以下的鏈狀結構: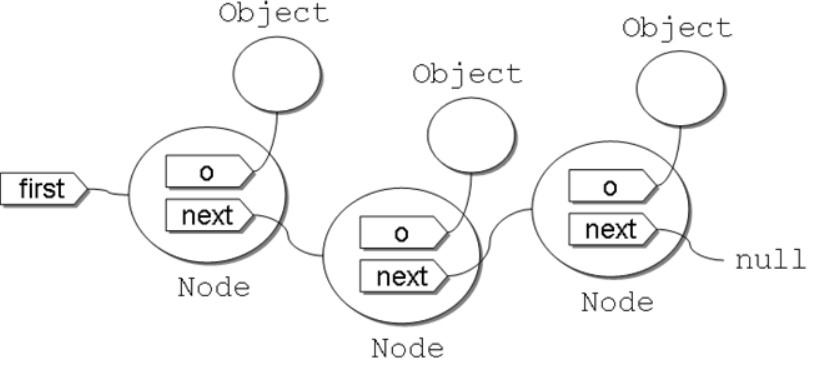
每次 add 物件時,才會建立新的 Node 來保存物件,不會事先耗費記憶體,若呼叫 size,則從第一個物件,逐一參考下一個物件並計數,則可取得收集的物件長度。若想呼叫 get 指定索引取得物件,從第一個物件,逐一參考下一個物件並計數,則可取得指定索引之物件。
特點
- 插入和刪除:在任何位置(包括頭部和尾部)插入或刪除元素的性能很好,因為這不需要移動其他元素。
- 隨機訪問:與 ArrayList 相比,隨機訪問(如 get(int index))性能較差,因為需要從頭或尾部遍歷列表來定位元素。
- 內存使用:每個元素都需要更多的內存,因為除了存儲數據外,還需要存儲前後元素的引用。
範例
1 | |
比較
| 特性 | ArrayList | LinkedList |
|---|---|---|
| 內部實現 | 基於動態數組(Array) | 基於雙向鏈表 |
| 隨機訪問 | 非常快(直接通過索引訪問) | 較慢(需要從頭或尾遍歷) |
| 添加操作 | 尾部添加快;中間或開頭添加慢(可能需要移動元素) | 在任何位置添加都很快(不需要移動其他元素) |
| 刪除操作 | 尾部刪除快;中間或開頭刪除慢(可能需要移動元素) | 在任何位置刪除都很快(不需要移動其他元素) |
| 內存使用 | 較少(只存儲數據本身) | 較多(存儲數據及前後元素的引用) |
| 性能 | 適合讀取操作多的場景 | 適合寫入操作多的場景 |
| 擴容 | 自動擴容,但擴容操作成本較高 | 無需擴容,添加/刪除操作通常不受現有大小限制 |
與Collection 的比較
Collection
定義
Collection 同時是 List, set, queue 的超級接口,並且定義了所有class 的基本操作,如添加、刪除、清空、大小、是否為空,
特點
- 一個更通用的接口,適用於各種集合類型。
- 不提供任何直接的實現,但它是實現任何具體集合類型的基礎。
- 使用 Collection 接口可以編寫更通用和靈活的代碼,因為它不依賴於特定的集合實現。
範例
1 | |
創建了一個 ArrayList 的實例,但宣告為 Collection。讓我們不用管是哪種具體的集合類型
AbstractList
定義:
為集合的一個 abstract class, 提供了 List 接口的骨架實現,從而最小化了實現此接口所需的工作。
用途:
當你需要實現一個自定義的列表時,你可以繼承 AbstractList 並實現其抽象方法
特點:
- 為實現 List 接口提供了一個方便的起點。
- 需要重寫 get(int index) 和 size() 方法。
- 可選地重寫其他方法以提高性能。
範例
假設我們要創建一個簡單的不可變列表,只允許讀取操作。
1 | |
在這個例子中,CustomList 繼承自 AbstractList,並實現了 get 和 size
參考文章:
感謝葛格https://openhome.cc/zh-tw/java/collection/hierarchy/
Java List 介紹
https://shengshengyang.github.io/2024/01/27/java-list/